구현
import java.util.*;
public class javatest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 정점의 개수
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 간선의 개수
int v = sc.nextInt(); // 탐색을 시작할 정점의 번호
boolean visited[] = new boolean[n + 1]; // 방문 여부를 검사할 배열
LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList = new LinkedList[n + 1];
// 링크리스트 안에 링크리스트 생성
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
adjList[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
// 두 정점 사이에 여러 개의 간선이 있을 수 있다.
// 입력으로 주어지는 간선은 양방향이다.
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int v1 = sc.nextInt();
int v2 = sc.nextInt();
adjList[v1].add(v2);
adjList[v2].add(v1);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Collections.sort(adjList[i]); // 방문 순서를 위해 오름차순 정렬
}
System.out.println("BFS - 너비 우선 탐색 시작");
BFS(v, adjList, visited);
}
// BFS - 너비 우선 탐색 시작
public static void BFS(int v, LinkedList<Integer>[] adjList, boolean[] visited) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
visited[v] = true;
queue.add(v); // 큐에 넣기
while(queue.size() != 0) {
v = queue.poll(); // 큐에서 꺼내기
System.out.print(v + " ");
Iterator<Integer> iter = adjList[v].listIterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
int w = iter.next();
if(!visited[w]) {
visited[w] = true;
queue.add(w);
}
}
}
}
}
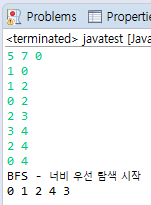
결과